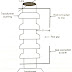
Watt-hour-meter structure:
⌲The construction of this relay is similar to the watt-hour-meter commonly used everywhere.
 |
| Structure Of Watt hour meter |
⌲It consists of E shaped electromagnet and a U shaped electromagnet with an aluminium disc free to rotate in between the upper electromagnet (E shaped) carries two windings, the primary and the secondary.
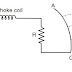
⌲Referring to show in fig: the primary winding carries relay current I, (also Known as C.T. secondary current) while secondary winding is connected to the winding of the lower magnet.
⌲The primary current induces e.m.f. in the secondary winding and circulates current I2 in it.
⌲The flux o, induced in the lower magnet by the current in the secondary winding of the upper magnet will lag behind 0, by an angle @.
⌲The two fluxes 1 and 2 differing in phase by a will produce a driving torque on the disc proportional to 01 02 sin a.
⌲The operation of this type of relay can be controlled by opening or closing the secondary winding circuit. If this circuit is opened, no flux can be set by the lower magnet, consequently no torque will be produced. Therefore, the relay can be made inoperative by opening its secondary winding circuit.


0 comments: