Type of Lightening Strokes
There are two main ways in which a lighting may strike the power system:
(a)Direct stroke.(b) Indirect stroke.
(a)Direct stroke:
☛In case of direct lightening stroke, the charge from the cloud is directly discharged on the object below it.
☛After discharging, the current finds the path through the insulator to the pole to the ground.
☛The over voltage set up due to the lightening stroke has a very large magnitude and may cause flashover or puncture of line insulator.
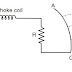
The direct strokes can be classified as:
1) Stroke A
2) Stroke B
 |
| Direct lightening stroke |
(i) Fig. shows the direct lightening stroke. It can be explained in two ways. Referring to first figure, suppose a overhead transmission line is exactly below the positively charged cloud and there is no more cloud near to this one, then the lightening discharge will occur from the cloud to the object (i.e. overhead line) below it. In this case the cloud will induce a charge of opposite sign on the tall object.
When the potential between the cloud and line exceed the breakdown value of air, the lightening discharge occurs between the cloud and the line.
(ii) Referring to second figure if there are three clouds P, Q and R having positive, negative and positive charge respectively then the charge on the cloud Q is bound by the charge on cloud R.
☛If the cloud P shifts too near the cloud Q, then lightening discharged will occur between them and a charge on both these clouds disappears quickly.
☛The result is that charge on cloud R suddenly becomes free and it then discharges rapidly to earth, ignoring tall objects.
☛i.e.in second case the lightening discharge occurs on the overhead line as a
result of stroke A between the cloud P and
(b) Indirect stroke:
☛The charged cloud always creates the equal and opposite charges on the object below it by the electrostatic action.
☛Assume that a positively charged cloud is exactly above the overhead line.
☛Thus it creates the negative charge of equal magnitude on it.
 |
| Indirect Lightening stroke |