Rod Gap Arrester: Construction & Working
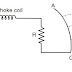
☛Rod gap arrester is a very simple type of surge diverter. Fig. shows the construction of rod gap arrester.
Construction Of Rod Gap Arrester
☛It mainly consists of two 1.5 cm rods, which are bent at right angles, and an air gap is provided in between them.
☛Upper rod is connected to the line circuit and the other rod is connected to earth.
☛While designing the rod gap arrester two important things should be taken in to
account. Firstly the distance between gap and insulator must not be less than one third of the gap length so that the are may not reach the insulator and damage it.
☛And secondly the gap length is so adjusted that breakdown should occur at 80% of spark- over voltage in order to avoid cascading of very steep wave fronts across the insulators.
Working Of Rod Gap Arrester
☛The operation of rod gap arrester is exactly same that of explained in previous section i.e. under normal operating conditions the gap remains non conducting.
☛On the occurrence of a high voltage surge on the line, the gap sparks over and the surge current is conducted to earth. Thus the excess charge on the line due to the surge is harmlessly diverted to earth.
 |
| Construction Of Rod Gap Arrester |
Limitation Rod Gap Arrester
(i) Due to the absence of non-linear resistance the arc in the gap is maintained by the normal supply voltage after the surge is over. This leads to a short circuit on the system.
(ii) Due to excessive heat produced by the arc, rods may melt.
(iii) Performance of rod gap arrester is depends on the climatic conditions such as rain, humidity, temperature etc.


0 comments: