Fluorescent Lamps: Principle, Construction & Operation
Principle Of Fluorescent Lamp
"When fluorescent materials are subjected to electromagnetic rediations of particular wavelength, they get excited and in turn gives out rediations at some other length, and persist in giving out rediations even if exciting rediations are removed".
Basic operation Fluorescent Lamp
Fluorescent lamps, in principle is low pressure mercury discharge lap with internal surface coated with suitable fluorescent material.
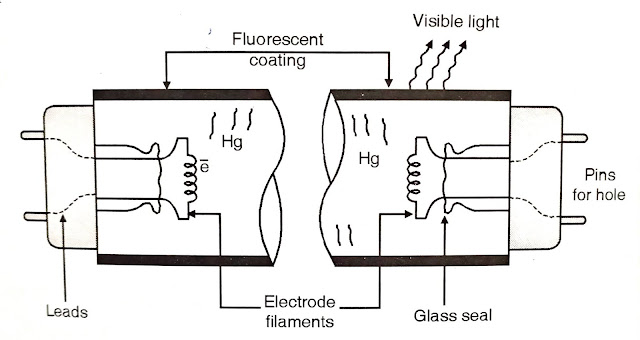 |
| construction of fluorescent tube |
Tube contains argon or krypton gas to case starting with small quantity of mercury under low pressure. At start, current is passed through filaments which get heated up and emit electrons which strike 'Hg' to give out rediations which fall on fluorescent material thus emitting light
Tube contains argon gas in small amount in vapour form and mercury in globular form i.e. not in pure vapour form. Argon gas is to initiate the arc.
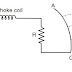
Circuit diagram for fluorescent lamps with :
- (a) Glow type starter :
- (b) Thermal Type Starter:
(a)Glow Type Starter:
✦In circuit diagram R and C are for protection purpose:
 |
| Tube With Glow Type Starter Circuit Diagram |
R-is to avoid welding of starter contacts and C-is to reduce radio interference.
✦Starter is made as two electrode E, and E, out of which E, is fixed and E₂ is of bimetallic strip. They are fitted into a glass tube having Helium and Hydrogen at low pressure.
✦Normally, the contacts E, and E, are open and when supply is applied full voltage is received by glow switch, this voltage is sufficient to start glow discharge between bimetallic strips E, and E, and heat generated bends E, to make contact with E, thus completing main circuit through choke and lamp electrodes A and B.
 |
| Glow Type Starter Working |
✦Current starts flowing through A and B and are heated in incandescence and argon gas which is in immediate vicinity is ionized by this time glow is shorted out and so E, and E, cools and contacts open again.
✦Sudden rate of change of current induced a voltage surge about 1000 V across choke and initiates a discharge of argon gas and heat is produced. This heat is sufficient to vaporize mercury and potential difference falls to 100 to 110 V.
(b) Thermal type starter :
✦Two bimetallic strips initially closed so that current flows through filaments, heater coil, thus the electrodes A and R are heated to incandescence and argon gas is ionized.
✦Meanwhile, one of the bimetallic strip near to heater coil gets heated and bends thus interrupting filament current producing inductive voltage surge across electron -establishing discharge through mercury vapour. Starting time is very much less than the flow type starter.


0 comments: