Essential Qualities Of Protection
As soon as the fault occurs on the power system, protection scheme should disconnect/isolate the faulty part as quickly as possible to minimize the damage to the system and to maintain the continuity of supply. Protective scheme may have following qualities :
1.Sensitivity:
Ability of the protective system to operate with low values of actuating quantity is known as sensitivity. The protective system should be enough sensitive to operate with the small quantity of fault current.
2.Speed:
As mentioned above, the protective system should disconnect the faulty part as quickly as possible for the following reasons:
- If the fault current is allowed to flow for the longer time then there will be considerable damage to the equipments which are feeding the fault.
- If the fault is not cleared quickly, then it is possibility of development of temporary fault in to permanent fault.
- If the faulty parts of the system are not cleared quickly then it is the possibility of spreading these faults into healthy parts of the system.
- A fault on the system causes the reduction in the terminal voltage, causing the complete shut down of consumer's motors. Also the generators on the system may become unstable.
3.Selectivity:
The ability of the protective system to select correctly the faulty part of the system and disconnect that part without disturbing the rest of the system is known as selectivity.
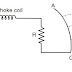
- Protective system should operate the circuit breaker which is nearer to the fault otherwise, opening of any circuit breaker to clear the fault will lead to disconnect the greater portion of the power system. Refering to Fig. if the fault occurs on the transmission line (which is located by point F), then operating of circuit breakers 6 and 8will cause minimum disconnection of the power system portion.
- In order to provide, selectivity to the system, the entire system is divided into several protective zones. When a fault occurs in a given zone, then only the circuit breakers within that zone be opened. This will isolate only the faulty section and the remaining healthy is unaffected.

Different Protective Zone

4.Reliability:
The ability of the protection system to operate under the predetermined conditions is known as reliability. The protection would be rendered largely ineffectively and could even become a liability without the reliability.
5.Simplicity:
A simple protective system is easy to maintain Reliability and Simplicity are closely related. The simpler the protection scheme, the greater will be its reliability.
6.Adequate ness:
Providing protection scheme for every abnormal condition is very costly. Therefore, protection provided for any machine should be adequate.
Adequate ness of protection is judge by following aspects :
- Cost of the machine and importance of the machine.
- Rating of the machine to be protected.
- Probability of abnormal conditions due to internal and external causes.
- Continuity of supply as affected by failure of machine.
- Location of protected machine.
7.Economy:
Cost is the most important factor in the choice of a particular protection scheme. As a rule, the protective gear should not cost more than 5% of its total cost. However, when the apparatus to be protected is of at most importance, then economic considerations are often subordinated to reliability.


0 comments: